Advantages
- Ultra-potent β2-adrenergic receptor agonist that stimulates cAMP production with sub-nanomolar potency (EC50 = 0.25nM)
- Biased signaling profile selectively activates Gαs-mediated cAMP signaling while avoiding β-arrestin2 recruitment, reducing receptor desensitization characteristic of traditional treatments such as albuterol
- Maintains a consistent bronchodilation response in human airway smooth muscle (HASM) cells over time unlike conventional agonist
Summary
Respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are commonly treated with β₂-adrenergic receptor agonists that activate intracellular signaling pathways to induce airway relaxation. However, current therapies are limited by progressive receptor desensitization, or tachyphylaxis, largely attributed to β-arrestin recruitment. This desensitization reduces therapeutic efficacy over time and complicates long-term disease management, resulting in suboptimal outcomes for patients who rely on bronchodilators for daily symptom control.
Our researchers have identified a novel agonist, denoted Compound A, which is 5-hydroxy-8-(1-hydroxy-2-(phenethylamino)ethyl)-2H-benzo[b][1,4] oxazin-3(4H)-one, shown in Fig1A, through in silico docking of a multimillion-member library and subsequent optimization of leads by synthesis of compounds with R group substitutions. Screening utilized CHO cells measuring cAMP and b-arrestin2 via transfected biosensors and human airway smooth muscle (HASM) cells measuring relaxation via magnetic twisting cytometry. Compound A activates the human β₂-adrenergic receptor with sub-nanomolar potency (cAMP, EC₅₀ = 0.25 nM) and is a full agonist when compared to ISO (Fig 1B). However, unlike conventional balanced agents such as ISO, Compound A selectively activates Gαs-mediated cAMP signaling with minimal β-arrestin2 recruitment (Fig 1B). In HASM cells, Compound A elicits sustained airway relaxation without evidence of tachyphylaxis (loss of responsiveness with continuous exposure to agonist), offering a promising next-generation bronchodilator with extended therapeutic efficacy over existing β₂-agonists.
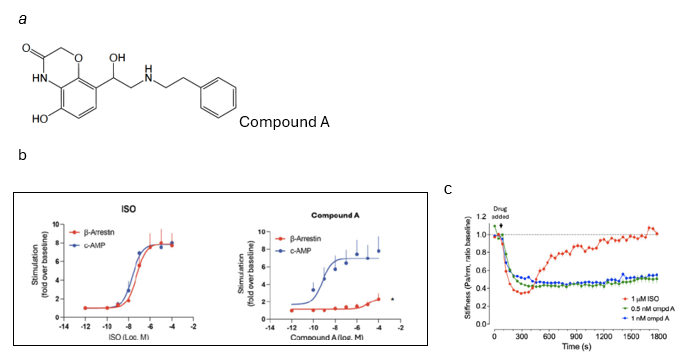
- Structure of compound A
- Stimulation of cAMP (blue graphs) and b-arrestin2 (red graphs) by ISO or Compound A. *, P<0.001 vs cAMP maximal response
- In this model where HASM relaxation is measured by magnetic twisting cytometry, continuous exposure to ISO (red graph) shows diminished relaxation in HASM cells over time (tachyphylaxis), while two concentrations of Compound A (blue and green graphs) maintain stable relaxation responses even at the 0.5 nM concentration
Desired Partnerships
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development