Advantages:
- Mitigates specular reflections that degrade radar performance
- Uses low-cost, distributed repeater elements to improve target detection
- No need for time or phase synchronization, enabling easy deployment
- Enhances image quality and resolution in challenging environments
Summary:
Millimeter-wave (mmWave) radar systems are widely used for high-resolution imaging in fields like automotive sensing, medical diagnostics, and security. However, these systems struggle with specular reflections mirror-like bounces where the reflected signal doesn’t return to the receiver. This causes weak returns, image degradation, and missed detections, especially for smooth or angled surfaces. Traditional solutions require complex multistatic architectures or distributed radars with costly synchronization between nodes.
This technology introduces a scalable and efficient method for detecting specular targets using distributed repeater apertures. These low-cost, mmWave repeaters capture the deflected radar energy and retransmit it toward the main receiver, significantly improving signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), image contrast, and detection accuracy. Experimental and simulated results across 36–38 GHz show the system enhances detection by more than 16 dB, clearly resolving targets that conventional radar misses. This repeater-based architecture is simple to integrate and highly adaptable, making it ideal for use in autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, and smart sensors.
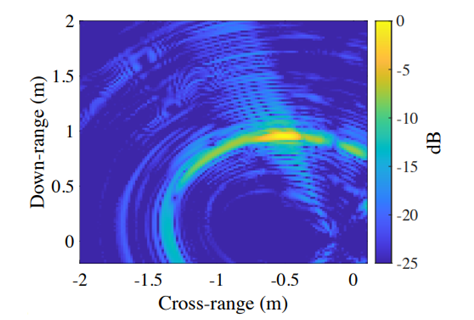
This experimental radar image demonstrates the improved target detection achieved using distributed repeaters. Compared to traditional setups, the system produces a clearer, high-contrast image overcoming the signal loss caused by specular reflections.
Desired Partnerships:
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development