Advantages:
- Non-invasive administration of PAMAM Dendrimer-based eye drop formulation eliminates risks associated with needle-based procedures and reduces cost
- Hyaluronic acid (HA) on the Dendrimer surface targets overexpressed CD44 receptors on retinal cells, potentially leading to higher bioavailability in the posterior eye
- Encapsulation of poorly soluble therapeutics in β- or γ-cyclodextrin before conjugation to the Dendrimer, Improved solubility of drugs
- Functionalized PAMAM Dendrimer avoids enhancers like penetratin and reduces systemic absorption and off-target toxicity
- Generation 4 (G4) PAMAM Dendrimer has a proven track record of safety and size consistency, reducing concerns about immunogenicity and biocompatibility
Summary:
Delivering therapeutics to the posterior segment of the eye via topical administration faces multiple obstacles, including poor ocular surface adherence, limited bioavailability, rapid lacrimal drainage, and the protective barriers of the cornea, sclera, and retina. Current approaches such as intravitreal injections offer more direct access to the retina but are invasive and come with potential safety concerns. To address these issues, a variety of polymeric and lipid-based nanomaterials are under investigation, with dendrimers emerging as a promising platform due to their well-characterized branching structure and “proton sponge” effect that aids endosomal escape. Despite their potential, dendrimers in topical formulations have produced inconsistent results, often requiring penetration enhancers that can cause controversial outcomes and off-target effects. Moreover, drug solubility challenges and restricted transport through ocular barriers further limit therapeutic efficacy.
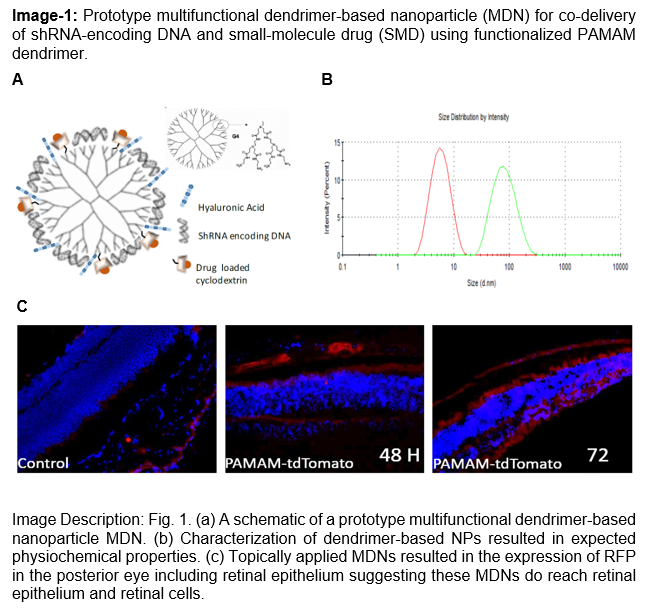
Modified Generation 4 (G4) poly (amidoamine) dendrimers serve as the core of a non-invasive topical platform for delivering gene and drug therapies to the posterior eye. These dendrimers are complexed with plasmid DNA encoding short hairpin RNAs at a 1:5 ratio, which increases the particle size from around 10 nm to 70 nm, and poorly soluble drugs are first encapsulated in cyclodextrin before conjugation to the dendrimer surface. The hybrid nanoparticles are further functionalized with hyaluronic acid (HA) to target CD44 receptors on retinal cells, while the remaining amine groups are PEGylated to enhance colloidal stability. Characterization by dynamic light scattering and electron microscopy confirms size and morphology, in vitro uptake and gene silencing are assessed in murine and human cell lines, and in vivo studies demonstrate drug release and posterior eye distribution following topical application.
Desired Partnerships: