Advantages:
- Semi-high throughput screening accelerates drug discovery by quickly identifying candidates, reducing time to market, and gaining a competitive edge.
- Molecular Chaperone reduces tau aggregation, preserving cognitive function and improving patient quality.
- Employs a precision medicine approach targeting tauopathy mechanisms, potentially offering more personalized and effective treatments than traditional therapies.
Summary:
The aberrant accumulation and aggregation of tau protein plays a central role in the progression of tauopathies, like Alzheimer's. This progression is driven by tau seeding, where misfolded tau induces further misfolding and aggregation, spreading pathology across brain regions. Molecular chaperones, which assist in the folding and stability of other proteins, have been identified as potential regulators of tau aggregation and toxicity. However, the specific interactions and pathways these chaperones influence tau pathology remain largely unexplored.
Our researcher conducted a semi-high throughput screen to identify molecular chaperones influenci tau seeding in an in vitro tauopathy model, using Tau RD P301S FRET Biosensor cells. They discovered that the molecular chaperons of the DnaJ family, particularly DnaJB6b, significantly reduced tau levels. Mechanistic studies revealed that DnaJB6b likely reduces tau levels by enhancing proteasomal degradation. This research highlights a new potential therapeutic intervention for tauopathies, by utilizing DnaJB6b to decrease tau levels in the brains of patients.
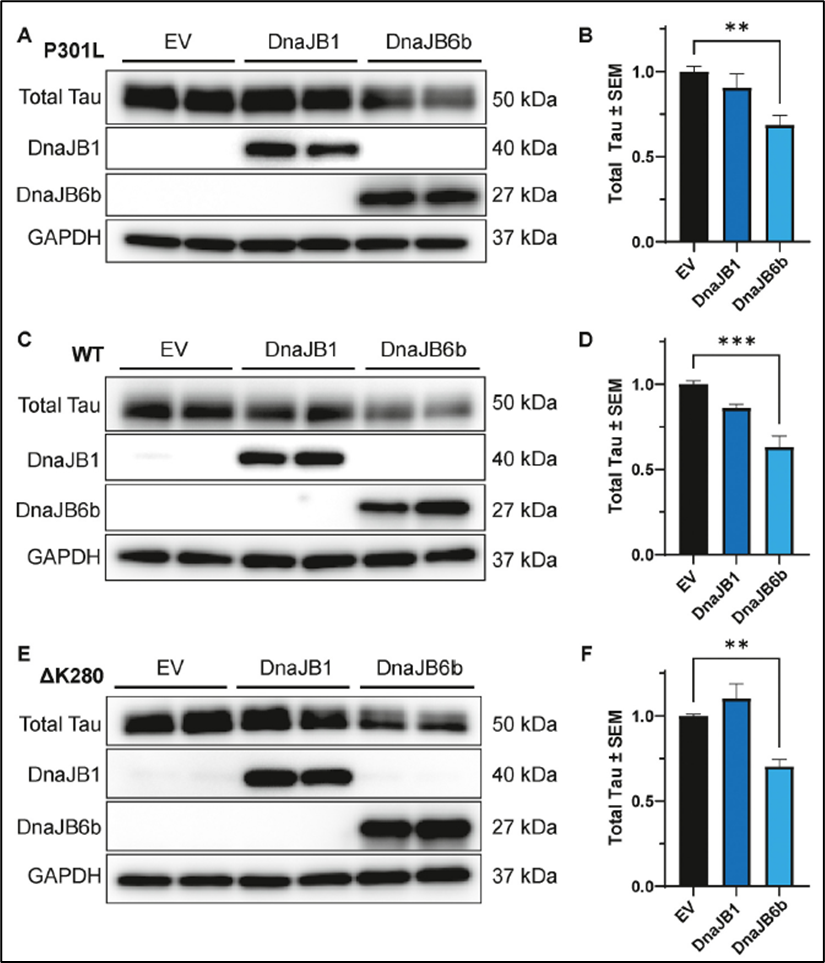
The image shows that overexpression of DnaJB6b reduces tau levels in iHEK P301L, WT, and ΔK280 tau cells. Tau expression was induced with tetracycline for 48 hours, followed by transfection with DnaJB1, DnaJB6b, or an empty vector (EV) control for an additional 48 hours. Western blot analysis of cell lysates was conducted, with representative images and quantification of tau levels relative to GAPDH shown for iHEK (A-B) P301L, (C-D) WT, and (E-F) ΔK280 tau cells. Quantification of total tau, normalized to the EV control, was averaged from two independent experiments ± S.E.M. Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test, with significance levels indicated as: **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Desired Partnerships:
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development