Advantages:
- High Precision and Accuracy: AI algorithms and GMM to accurately identify mosquito larvae genus and species, reducing misidentification risks in critical applications like vector-borne disease control.
- Granular Analysis: Detailed analysis of mosquito larvae anatomy, enabling genus and species classifications for each localized component, aiding researchers in in-depth studies of mosquito populations and behaviors.
- Explainable AI: GMM enhances transparency in identification processes, providing users with a better understanding of classifications, and making it a valuable tool for researchers and decision-makers.
Summary:
Our innovative solution combines cutting-edge algorithms and geometric morphometrics (GMM) techniques to revolutionize the identification of mosquito larvae genus and species. Our AI-powered algorithms precisely localize and extract core anatomical components from mosquito larvae, creating detailed masks for analysis. Leveraging fine-grained AI algorithms, we provide genus and species classifications for each localized/masked component. This approach ensures highly accurate and granular results. Additionally, our incorporation of GMM adds an element of explainable AI, enhancing the transparency of our identification process. This breakthrough technology has vast applications in vector-borne disease control, environmental monitoring, and research, offering a powerful tool for entomologists, public health officials, and researchers worldwide.

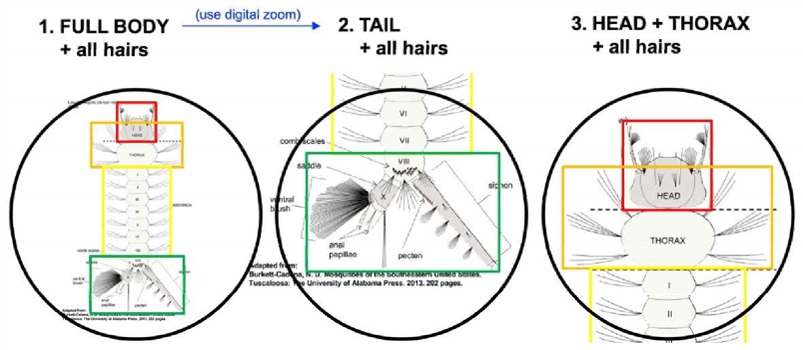
Figure 1: 2D geometric morphometric method, illustrating the setae-based landmarks (white dots) for the various anatomical regions (color-coded masks) of a mosquito larva.
Figure 2: Bounding box method for localization of individual anatomical regions.
Desired Partnerships:
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development