Advantages:
- Exceptional precision in addressing inflammation, minimizing potential side effects.
- Unique COX-2 interaction reduces the risk of adverse reactions.
- Versatile effectiveness across various inflammatory disorders, providing relief to a wide range of patients.
Summary:
This technology addresses a significant healthcare challenge related to the management of inflammation and its associated disorders, particularly pain. Inflammation, which represents a complex biological response, plays a pivotal role in various medical conditions, often leading to discomfort, pain, and occasionally irreversible tissue damage. This innovative approach revolves around the administration of a meticulously formulated composition containing a unique compound referred to as formula (I). The primary objective of this technological advancement is to tackle various forms of inflammation, encompassing both acute and chronic cases. It also extends its applicability to a wide range of inflammatory disorders, including but not limited to arthritis, gastrointestinal issues, and vascular diseases.
At its core, formula (I) demonstrates noteworthy inhibitory activity against tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), a pivotal mediator of inflammation. What sets this novel compound apart is its minimal to negligible inhibitory effect on cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), thereby distinguishing it from conventional anti-inflammatory drugs. This technological advancement holds the promise of enhancing precision in targeting inflammation, potentially mitigating the associated side effects linked to COX-2 inhibition. Consequently, it emerges as a potential safer and more efficacious solution for individuals in need. The compound's selectivity and potency in modulating inflammation pathways hold substantial potential for future pharmaceutical development, thereby offering new prospects for personalized anti-inflammatory therapies.
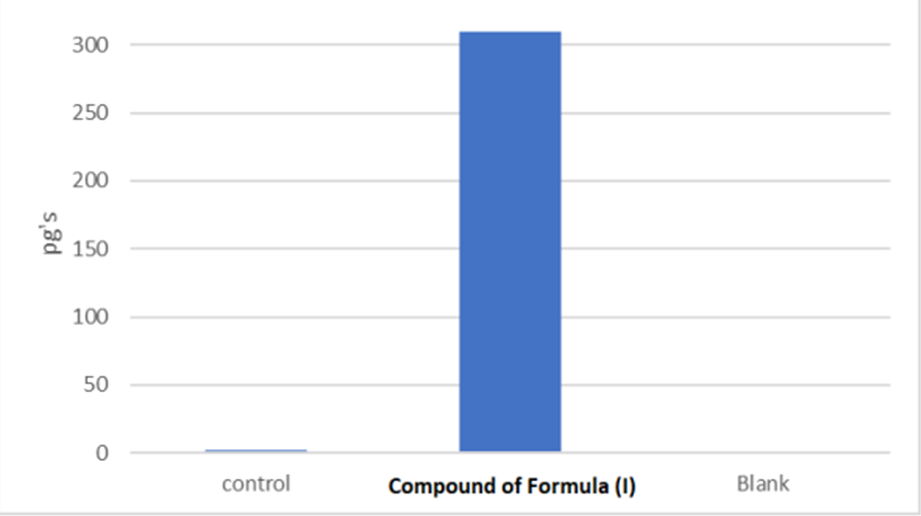
Shows a COX-2 assay comparing compound (I) to diclofenac and a control (dimethyl sulfoxide). Compound (I) exhibits minimal COX-2 inhibitory activity in contrast to diclofenac, indicating its limited anti-inflammatory potential.
Desired Partnerships:
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development