Advantages:
- The study highlights FKBP51 as a promising target for the treatment of disorders such as major depression, PTSD, anxiety disorders, and Alzheimer's disease.
- The research recognizes the influence of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the FKBP5 gene on FKBP51 levels and susceptibility to certain disorders.
- The researchers have identified lipid derivatives that can prevent the upregulation of FKBP51 in response to stress. The advantage of using these compounds is that they are naturally found in the body, which may facilitate their development into clinically applicable treatments.
Business Summary:
The FK506-binding protein (FKBP51) is an important co-chaperone of the 90 kDa heat shock protein (Hsp90) machinery. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in FKBP5 gene, coding for FKBP51, can combine with stress to elevate FKBP51 levels and increase risk for major depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and anxiety disorders. FKBP51 levels also increase with age and are further elevated in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients.
Our researchers have identified three fatty acid derivatives (FADs) that prevent the upregulation of FKBP51 following stress. Thus, patient groups with PTSD, AD, anxiety disorders etc. could benefit from ablating stress induced FKBP51 using these FADs or their synthetically modified forms.
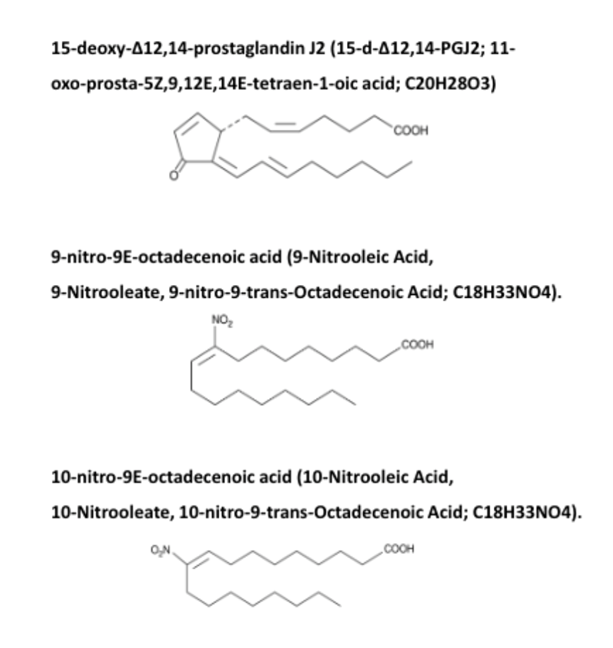
Chemical structure of 15-deoxy-12,14-prostaglandin J2, 9-nitro oleic acid and 10-nitro oleic acid
Desired Partnerships:
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development