Competitive Advantages:
- Novel method to isolate, cultivate, and amplify the lung microbiome from a limited resource
- Beneficial for testing antibiotic sensitivity and drug resistance
- Enables lung microbiome transplantation for treatment of various chronic lung diseases
Summary:
Chronic lung diseases such as asthma, COPD, cystic fibrosis, or lung transplant patients critically depend on a beneficial lung microbiome as part of the healing process and/or to revert their chronic lung disease. Hence the favorable modulation of lung microbiota obtained from healthy donors may impact the host immune response to reduce progression of lung diseases. Since the microbiome of the lung has relatively less bacterial biomass when compared to the lower gastrointestinal tract it is difficult to obtain sufficient quantities of lung microbiome samples for direct clinical analysis.
Our researchers have developed a procedure for the isolation and cultivation of lung microbiome from patients with chronic lung diseases. Bronchoalveolar lavage was used to isolate and subsequently cultivate and amplify the lung microbiome from patients based on three different media that allow the growth of aerobic and fastidious anaerobic lung bacteria. This novel procedure to isolate, cultivate, and amplify the lung microbiome of patients to sufficient quantities can have several applications, including microbiome testing in a clinical laboratory setting, antibiotic sensitivity testing, drug resistance testing, and amplification and transplantation of naturally occurring lung microbiome.
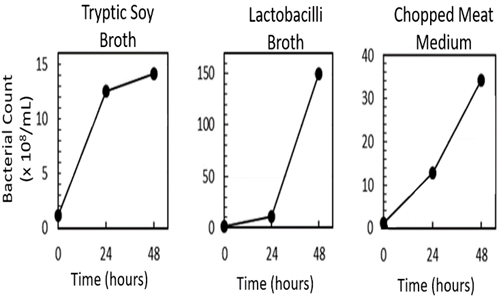
Lung Microbiome Cultivation Using Various Media
Desired Partnerships:
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development