Advantages:
- Automatically analyzes 3D brain scans across multiple imaging modalities
- Detects and quantifies ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke volumes
- Identifies distal vessel occlusions using CT-angiography segmentation
- Provides a quantitative foundation for diagnosis, treatment planning, and follow-up
Summary
Stroke diagnosis is time-critical, but analyzing complex 3D imaging data like CT and MRI can delay treatment decisions. Clinicians must rely on manual interpretation, which is time-consuming and often lacks quantitative precision especially when tracking subtle changes in stroke size, location, or etiology.
This AI-enhanced imaging system solves that by using a semi-automated MATLAB pipeline and high-performance computing to extract and process multidimensional stroke imaging data. It processes DICOM files, segments ischemic or hemorrhagic regions, and detects vessel abnormalities using CT angiography. The system enables real-time triage, quantification, and trend analysis, helping physicians detect branch occlusions and measure changes over time. This platform is designed to become a clinical biomarker for cerebrovascular disease, improving stroke management across diagnosis, intervention, and recovery.
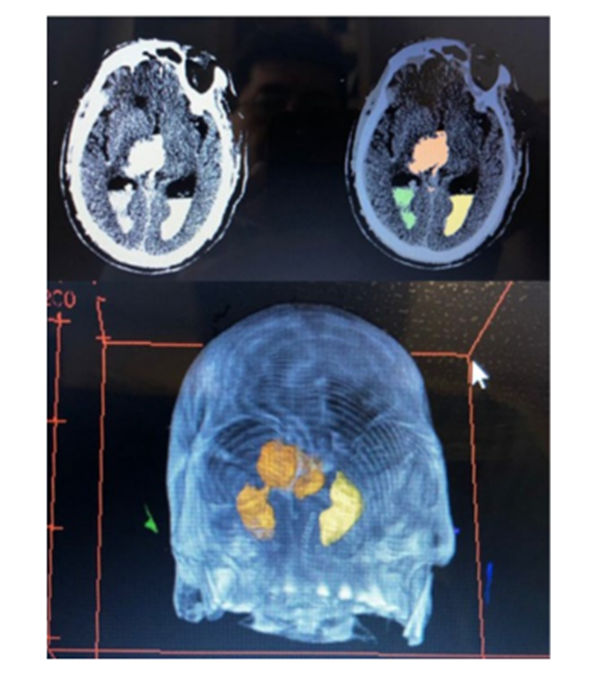
This figure shows AI-enhanced brain imaging of stroke patients. The top row displays CT scan slices with color-coded regions highlighting infarcted (damaged) brain tissue. The bottom image presents a 3D reconstruction of the same infarcted areas, enabling more precise visualization of stroke volume and location. This advanced imaging assists physicians in faster diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of stroke progression or recovery.
Desired Partnerships
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development