Competitive Advantages
- May slow or stop Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease progression
- Disrupts beta-sheet aggregation
- Can treat several neurodegenerative disorders
Summary
USF researchers have developed an innovative method to disrupt amyloid aggregation for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and related disorders. This invention includes the synthesis and development of short N-aminated peptides. These backbone aminated peptides mimic beta-sheet protein secondary structure and effectively disrupt beta-sheet association and aggregation events important in the progression of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other related diseases.
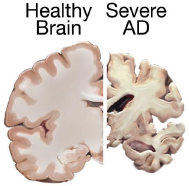
A Visual Example Showing the Effects of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) on Brain Matter
Desired Partnerships
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development