Competitive Advantages
- No additional power, area and performance overhead
- Immune to machine learning attacks
- Nonzero power trace entropy
- Decorrelates number of activated switch phases from load power consumption
Summary
Our researchers have developed a power, area, and performance efficient countermeasure against differential power analysis (DPA) attacks. The method developed by USF engineers randomly reshuffles the individual stages within a multiphase switched-capacitor voltage converter. The randomized reshuffling of the converter stages inserts noise to the monitored power profile and prevents an attacker from extracting the correct input power data. Additionally, a charge-withheld CoRe technique is used to withhold a random amount of charge for a random time period. This breaks the one-to-one relationship between the monitored and actual power consumption. This technique eliminates the possibility of having a zero power trace entropy (PTE), which is an improvement over conventional methods. The method efficiently protects the secret key in a cryptographic device.
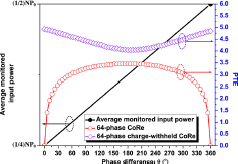
PTE Comparison for Conventional CoRe and Charge-withheld CoRe Techniques
Desired Partnerships
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development