Competitive Advantages
- Strong bactericidal activity with limited damage toward human cells
- Proven effective against drug-resistant MRSA
- Low incidence of resistance by A. baumannii vs. competitive compounds
Summary
Researchers at the University of South Florida have identified compounds that have proven to be effective against Acinetobacter baumannii, a pathogen known to be resistant to multiple existing antibiotics.
They previously determined that N2,N4-disubstituted quinazoline-2,4-diamines proved effective in disrupting biofilms as well as cell membrane structure of both E. coli and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), targeting the bacterial DHFR enzyme critical to DNA replication in vitro as well as in vivo for murine models. It also possesses anti-biofilm properties and is minimally cytotoxic in humans. These facets together make N2,N4-disubstituted quinazoline-2,4-diamines a fantastic anti-A. baumannii drug.
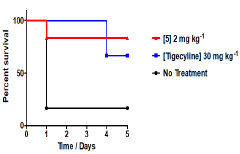
Lead Quinazolines are Efficacious in a Murine Model of A. Baumannii Lethal Peritonitis
Desired Partnerships
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development