Competitive Advantages
- Energy-aware authentication protocol suitable for IoT devices and embedded devices
- Provable Security standards to the level of upcoming post-quantum security breaches in cryptosystems
- Scalable security architecture support for massive IoT applications
Summary
IoT devices play a central role in the distributed systems for data collection, diagnosis, and analysis, especially in medical wearable devices and intelligent home-based applications. In the future, there would be an exponential increase in the number of such devices and hence the risk of their owner’s data getting compromised. Data protection is an issue of paramount importance, but the resource-limited structure (battery, CPU, memory) makes it challenging to implement appropriate security for such devices. Our technology, referred as HASOS-F, precisely addresses this problem with the help of a cryptographic mechanism.
The novel feature of this technology is that it considers the resource limitation and provides advanced user-centric security features like forward-security, aggregation, multi-signature, and post-quantum security. It is possible by designing the system around heterogeneous IoT systems, so the heavy resource-eating tasks (like signing) could be assigned to the resource-rich devices, like laptops in the network, and provide protection to resource-limited devices. This heterogeneous approach enables low signing costs by harnessing hardware support to authorize verification and interactions. The interaction between multiple devices, enhanced signature scheme, public commitments, and keys plays a significant role in this system and method, which in turn help to reduce cost resource for limited capability IoT devices with increased security and protection of user data.
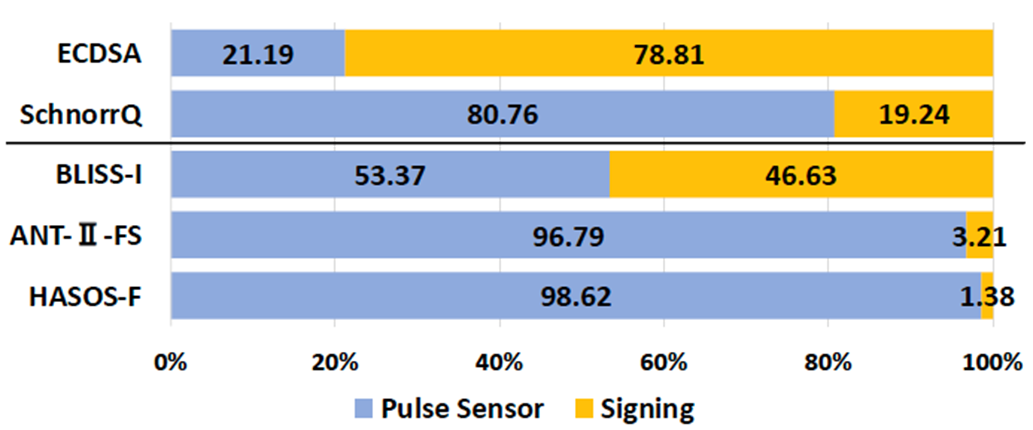
Energy Consumption of signing vs pulse sensor, HASOS-F outperforms all alternatives and also offers forward security. Unlike ANT-II-FS, it does not need non-colluding servers.
Desired Partnerships:
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development