Competitive Advantages
- Highly scalable processing methods
- Wide range of tunable dimensions
- High specific strength
- High damage tolerance
Summary
USF inventors have demonstrated the feasibility of template electrodeposition of crystalline and amorphous alloy nano-rods, micro -tubes and micro-pillars with tunable sizes and compositions. The method offers an opportunity to fabricate low areal density aluminum alloy microstructures using a one-step electrodeposition process using a room temperature ionic liquid electrolyte under galvanostatic control. The composition of the microstructure can be altered by changing metal concentration within the electrolyte, thereby introducing intrinsic scalability, and this presents immediate contribution in applications, such as plasmonic pixels in color display, anodes for Li-ion batteries, or energy adsorbers. The open architecture provided by the invented structures also provides channels for heat and fluid flow, which are critical to multi-functional devices, such as high capacity batteries, insect-like robots, and micro-air vehicles.
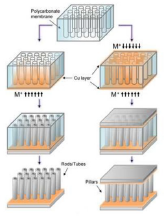
Schematic of Deposition Procedures for Nano-Rods, Micro-Tubes and Micro-Pillars
Desired Partnerships
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-development