Advantages
- Safe and Effective
- Allows for targeting of deep tissue cancer cells
- Uses the already effective NIR-PIT
Summary
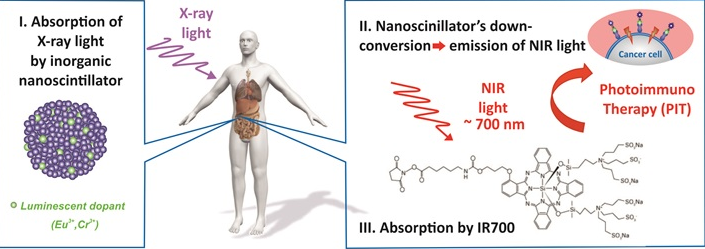
Our researchers have developed a method to bring IR light, and thus NIR-PIT, to deeper layers of tissues. NIR-PIT (Near IR Photo Immune Therapy) works via the attachment of an antibody to the cancer cell membrane. An attached APC is then activated, using IR light, which disrupts the cancer cell membrane, thus only killing cancer cells. Proven to be nearly 100% effective for surface head-neck tumors that are otherwise untreatable, this invention allows for deep-tissue treatments for such pernicious cancers as liver, pancreas, etc. whereby cancer cells are distributed throughout the organ, rather than brain caner which is often contained in a tumor bed that can be surgically removed. This method uses silicon carbide (SiC) nanostructures capable of converting x-ray photons from a traditional hospital source, such as a CT scanner, into NIR light to activate the cancer-killing complex in deeper tissue. This would allow for the targeted and safe treatment of cancer cells and growths in areas were normal NIR-PIT could not reach on its own. IR-700 is the NIR sensitive receptor that, when illuminated, triggers the cancer killing process.
Graph Showing SiC nanoparticle near IR emission Overlapping With IR700 Emission, Transferring Energy from the Nanostructures to IR700 at Higher Wavelengths (nm)
Desired Partnerships
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development