Competitive Advantages
- Applicable to a wide range of diseases with endothelial dysfunction
- Targets the cause not just the symptoms of allergies and pulmonary diseases
- Protects against cellular damage
- Reverses harmful effects of hyperoxic injury
Summary
Pulmonary diseases are characterized by endothelial dysfunction and changes in vascular permeability. Specifically, in acute lung injury, hyperoxia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction causes elevation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the deterioration of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) in pulmonary vascular endothelial cells
Our inventors have identified a new target and therapeutic approach for allergic and pulmonary diseases. They discovered that Alda-1 is a novel specific activator of ALDH2 in vascular endothelial cells. Alda-1 amplifies ALDH2 activity, shields against cellular damage in diseases such as heart failure and attenuates endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary diseases. Thus Alda-1 mediated modulation of ALDH2 results in the remediation of endothelial dysfunction through preservation of mitochondria. This can be novel and effective treatment for pulmonary and allergic diseases where endothelial dysfunction is a characteristic event.
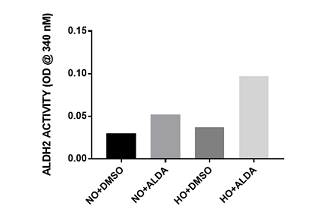
Cells Treated with Alda-1 Display Elevated ALDH2 Activity During Both Normoxia and Hyperoxia
Desired Partnerships
- License
- Sponsored Research
- Co-Development